Why You Need Antioxidants

What Are Antioxidants?
They’re chemicals that fight a process in your cells called oxidation. The main source is plant-based foods, but your body makes some, too. You’re probably familiar with vitamins C and E, beta-carotene, and the minerals selenium and manganese. Plant nutrients and chemicals like flavonoids, phenols, polyphenols, and phytoestrogens are also antioxidants.
Swipe to advance
2
/
12
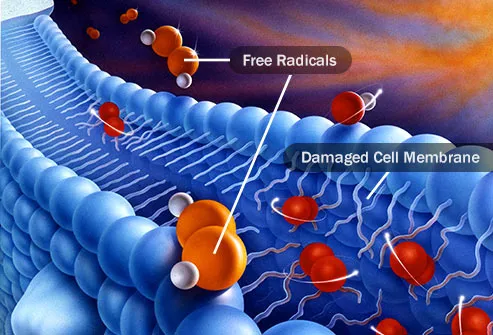
What Do Antioxidants Do?
Each one works differently. Together they form a team that fights free radicals. These chemicals cause the oxidation process that damages your cells and the genetic material inside them. Your body makes free radicals as it processes food, sunlight, and toxins like smoke, pollution, and alcohol. Antioxidants either stop free radicals before they form or break them down so they’re harmless.
Swipe to advance

3
/
12
Vitamin E
This antioxidant is stored in fat (you may hear it called fat-soluble). It fights off free radicals that attack fats in your cell walls. It may also stop LDL cholesterol from turning into a form that could harden your arteries (your doctor may call it oxidized) and lead to cardiovascular disease.
Where to get it: Whole grains, vegetable oils (olive, sunflower, canola), nuts, and green leafy vegetables.
Swipe to advance

4
/
12
Vitamin C
Also known as ascorbic acid, it’s stored in water (you may hear it called water-soluble). It may help prevent cancers of the stomach, lung, and digestive system.
Where to get it: Green vegetables, tomatoes, and citrus fruits like oranges and grapefruits. Choose raw foods because cooking may destroy it.
Swipe to advance

5
/
12
Beta-carotene
It’s a fat-soluble carotenoid (those are the yellow, orange, and red pigments in vegetables and fruits). Your body turns it into retinol, which helps you see. It may be dangerous when taken in supplement form, so it’s best when it comes from food.
Where to get it: Fruits, grains, carrots, squash, spinach, and other green vegetables.
Swipe to advance

6
/
12
Lycopene
This carotenoid may help protect against prostate, lung, and breast cancer.
Where to get it: Cooked and processed tomatoes are a good and common source: Think marinara sauce on your pasta. Heating the tomatoes makes it easier for your body to absorb the lycopene. Add a bit of fat like olive oil to further help your body use this nutrient.
Swipe to advance

7
/
12
Selenium
Found in soil and water, this mineral helps your thyroid work. Research suggests it can help protect against cancer, especially of the lung, colon, and prostate. It’s easy to get too much if you take it as a supplement. That can lead to digestive problems, hair and nail loss, and even cirrhosis of the liver.
Where to get it: Grains, onions, garlic, nuts, soybeans, seafood, meat, and liver.
Swipe to advance

8
/
12
Flavonoids
Scientists know about more than 4,000 of these antioxidants found in fruits and veggies. Every plant contains a different flavonoid combination. They may help protect against heart disease, cancer, arthritis, aging, cataracts, memory loss, stroke, inflammation, and infection.
Where to get them: Green tea, grapes, red wine, apples, chocolate, and berries.
Swipe to advance

9
/
12
Omega-3 and Omega-6 Fatty Acids
Omega-3s help protect against heart disease, stroke, arthritis, cataracts, and cancer. Omega-6s help improve eczema, psoriasis, and osteoporosis. You should get about two to four times more omega-6s than omega-3s to keep them in balance. Your body can’t make these essential fatty acids, which help stop inflammation. There are supplements, but it’s better when they come from food.
Where to get them:
- Omega-3s: Salmon, tuna, sardines, walnuts
- Omega-6s: Vegetable oils, nuts, poultry
Swipe to advance

10
/
12
Can’t You Just Take a Pill?
Nope. Long-term studies on tens of thousands of people show that antioxidants in pill form don’t lower your odds of bad health. People who took them got heart disease, cancer, and cataracts at the same rate as those who didn’t. One exception is age-related macular degeneration. Antioxidant supplements slowed progress a little for some people in late stages of this eye disease.
Swipe to advance

11
/
12
Are Fruits and Veggies the Secret?
Sort of. Vegetables and fruits have lots of antioxidants. And it’s true that if you eat more of them, you’re less likely to get any number of diseases. What isn’t clear is why. It may be the antioxidants, or it might be other chemicals in those foods. It could even be that people who eat them make healthier lifestyle choices overall. Scientists continue to explore the issue.
Swipe to advance

12
/
12
Too Much of a Good Thing?
It’s hard to get too many antioxidants from the food you eat. That isn’t the case, however, for those in supplement form. Too much beta-carotene may raise your lung cancer risk if you smoke. Too much vitamin E could make you more likely to get prostate cancer or have a stroke. These products can also change the way certain medicines work. Tell your doctor about any you take to make sure they don’t get in the way of your medication.
Swipe to advance
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps