Telltale Signs of Alzheimer’s
Could It Be Alzheimer's?
It’s normal for people to become a bit forgetful as they age. So how can you tell a harmless "senior moment" from Alzheimer's disease? One in eight people 65 and older have this devastating form of dementia. In its first stages, Alzheimer’s may not be obvious to friends and family. But there are some early warning signs to watch for.
Warning Signs: Memory and Speech
In early Alzheimer’s, long-term memories usually remain intact while short-term memories become sketchy. Your loved one may forget conversations you had. She may repeat questions that were already answered. The disease also disrupts speech, so she might struggle to remember common words.
Warning Signs: Behavior
In addition to memory loss, Alzheimer’s can cause confusion and behavior changes. Your loved one may get lost in familiar places. Mood swings and lapses in judgment are also common, as is poor hygiene. People who were once stylish may start wearing stained clothes and forget to wash their hair.
Don't Ignore the Signs
It's hard to face the thought that a loved one could have this disease, but it's better to see a doctor sooner rather than later. First, the diagnosis might be something else. The symptoms could be caused by a highly treatable problem, like a thyroid imbalance. And if it is Alzheimer’s, treatments work best when they’re used early in the course of the disease.
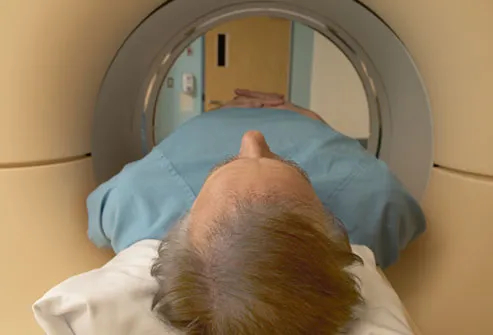
How Is It Diagnosed?
There’s no simple test for Alzheimer’s, so the doctor will rely on you to describe the changes in your loved one. A mental status test, sometimes called a “mini-cog,” or other screening tests can measure his mental skills and short-term memory. Neurological exams and brain scans may be used to rule out other problems, like a stroke or tumor, and they can provide other information about his brain.
What Happens to the Brain?
Alzheimer’s causes nerve cell death and tissue loss throughout the brain. As the disease gets worse, brain tissue shrinks and areas that contain cerebrospinal fluid become larger. The damage harms memory, speech, and comprehension.
What to Expect
Alzheimer’s takes a different path in every person. Sometimes the symptoms get worse quickly and lead to severe memory loss and confusion within a few years. For other people the changes are gradual. It could take 20 years for the disease to run its course. Most people live 3 to 9 years after diagnosis.
How Will It Change Daily Life?
Alzheimer’s affects concentration, so your loved one may not be able to do ordinary tasks like cooking or paying the bills. A study suggests trouble balancing the checkbook is often one of the first signs of the disease. As symptoms worsen, he may not recognize familiar people or places. He may get lost easily or use utensils improperly, like combing his hair with a fork. Incontinence, balance problems, and loss of language are common in advanced stages.
Should My Loved One Stop Driving?
Poor coordination, memory loss, and confusion are a dangerous combination behind the wheel. If you feel your loved one should stop driving, tell her why. If she won’t listen, ask her doctor to step in. If she still insists on driving, contact the Department of Motor Vehicles for an assessment. Then make other plans for her transportation needs.
Can Exercise Help?
Physical activity can help your loved one keep some muscle strength and coordination. It might also boost his mood and help him feel less anxious. Check with his doctor to learn which types of exercise are appropriate. Repetitive activities, like walking, gardening, or even folding laundry may be the best at giving him a sense of calm.
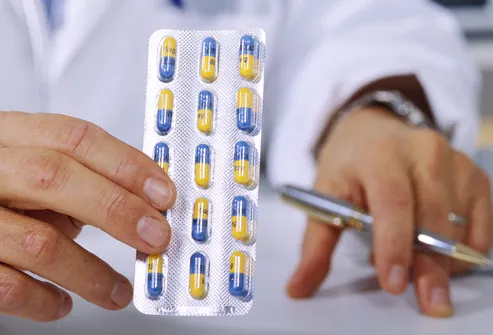
How Is It Treated?
There’s no cure for Alzheimer’s and no way to slow the nerve damage it causes in the brain. But there are medications that appear to help maintain mental skills and slow the disease’s effects. If your loved one gets treatment early on, she may be able to stay independent and do her daily tasks for a longer period of time.
The Caregiver's Role
If you’re caring for someone with this disease, you’ll probably wear many hats -- cook, chauffeur, and accountant to name a few. While you may have to handle meal planning and finances, encourage your loved one to do some things for herself. It may help to label cabinets with their contents and put up sticky notes with reminders of daily tasks. Be sure to buy a weekly pill box for her medications.
Challenges in Caregiving
In the early stages, people with Alzheimer’s often understand what’s happening to them. They may be ashamed or get anxious. Watch for signs of depression, which the doctor can manage with medication. Later on, your loved one may become paranoid or aggressive and could even turn on you. Remember that the disease is responsible for this change. Tell the doctor about this kind of behavior promptly.
Sundown Syndrome
Experts don’t know why, but some people with Alzheimer’s get upset when the sun goes down. This tends to last through the evening and sometimes all night long. To ease tension, keep the house well lit and close the drapes before sunset. Try to distract your loved one with a favorite activity or TV show. Switch him to decaf after breakfast.
When Your Loved One Doesn't Know You
Many people with Alzheimer’s have trouble remembering names, even of people closest to them. A temporary fix is to put up pictures of people they’re likely to see often or know well with names printed underneath. Eventually, your loved one may no longer recognize faces and may react as if family members are strangers. This can be distressing, especially for the main caregiver.
Warning Signs of Caregiver Stress
Caring for someone with Alzheimer's can be physically and mentally draining. Signs of caregiver stress include:
Anger, sadness, and mood swings
Headaches or back pain
Trouble concentrating
Trouble sleeping
Take Care of Yourself
To avoid caregiver burnout, make sure you take at least a few minutes to do something you enjoy every day. Stay in touch with friends and keep up with hobbies when you can. Find a friend or relative to be your support person. You can also join an online or local caregiver support group through the Alzheimer’s Association.
Essential Documents
While your loved one is still able to make important decisions, talk to an attorney about drafting advance directives. These are legal documents that spell out what he wants in terms of medical treatments and end-of-life care. He should name someone to make health care decisions and manage finances on his behalf. This will help avoid confusion later on if he’s no longer able to state his wishes.
Home Health Care
Many people want to stay in their own homes as long as possible. That’s not easy if they have trouble getting dressed or using the bathroom on their own. A home health aide can help with personal hygiene and other daily tasks. You can also check with your local Area Agency on Aging for information on services that deliver meals or provide transportation to the elderly.
Assisted-Living Facilities
There may come a day when your loved one can no longer be cared for at home. If she doesn’t need 24-hour nursing care, an assisted-living facility may be good choice. They provide housing, meals, and activities, but are much less expensive than nursing homes. Look for one with an Alzheimer’s special care unit that can give 24-hour supervision and personal care to meet the needs of people with dementia.
The Later Stages
People with advanced Alzheimer’s may lose their ability to walk, talk, or respond to others. Eventually, the disease can hinder vital functions, like the ability to swallow. This may be the time to switch to hospice care, which provides pain relief and comfort for people with terminal illnesses.
How to Help Children Understand
Children may feel confused, afraid, or even resentful when a family member has Alzheimer’s. Let the child know these feelings are normal and answer her questions about the illness honestly. Help her celebrate happy memories of your loved one. You could create a scrapbook with pictures from happier times.
Can You Prevent It?
Is there anything you can do to lower your chances of getting this disease? Research in this area is ongoing, but diet and exercise appear to be important. Studies show people who eat a Mediterranean diet rich in vegetables, fish, and nuts and get plenty of physical activity are the least likely to get Alzheimer’s.
It’s normal for people to become a bit forgetful as they age. So how can you tell a harmless "senior moment" from Alzheimer's disease? One in eight people 65 and older have this devastating form of dementia. In its first stages, Alzheimer’s may not be obvious to friends and family. But there are some early warning signs to watch for.
Warning Signs: Memory and Speech
In early Alzheimer’s, long-term memories usually remain intact while short-term memories become sketchy. Your loved one may forget conversations you had. She may repeat questions that were already answered. The disease also disrupts speech, so she might struggle to remember common words.
Warning Signs: Behavior
In addition to memory loss, Alzheimer’s can cause confusion and behavior changes. Your loved one may get lost in familiar places. Mood swings and lapses in judgment are also common, as is poor hygiene. People who were once stylish may start wearing stained clothes and forget to wash their hair.
Don't Ignore the Signs
It's hard to face the thought that a loved one could have this disease, but it's better to see a doctor sooner rather than later. First, the diagnosis might be something else. The symptoms could be caused by a highly treatable problem, like a thyroid imbalance. And if it is Alzheimer’s, treatments work best when they’re used early in the course of the disease.
How Is It Diagnosed?
There’s no simple test for Alzheimer’s, so the doctor will rely on you to describe the changes in your loved one. A mental status test, sometimes called a “mini-cog,” or other screening tests can measure his mental skills and short-term memory. Neurological exams and brain scans may be used to rule out other problems, like a stroke or tumor, and they can provide other information about his brain.
What Happens to the Brain?
Alzheimer’s causes nerve cell death and tissue loss throughout the brain. As the disease gets worse, brain tissue shrinks and areas that contain cerebrospinal fluid become larger. The damage harms memory, speech, and comprehension.
What to Expect
Alzheimer’s takes a different path in every person. Sometimes the symptoms get worse quickly and lead to severe memory loss and confusion within a few years. For other people the changes are gradual. It could take 20 years for the disease to run its course. Most people live 3 to 9 years after diagnosis.
How Will It Change Daily Life?
Alzheimer’s affects concentration, so your loved one may not be able to do ordinary tasks like cooking or paying the bills. A study suggests trouble balancing the checkbook is often one of the first signs of the disease. As symptoms worsen, he may not recognize familiar people or places. He may get lost easily or use utensils improperly, like combing his hair with a fork. Incontinence, balance problems, and loss of language are common in advanced stages.
Should My Loved One Stop Driving?
Poor coordination, memory loss, and confusion are a dangerous combination behind the wheel. If you feel your loved one should stop driving, tell her why. If she won’t listen, ask her doctor to step in. If she still insists on driving, contact the Department of Motor Vehicles for an assessment. Then make other plans for her transportation needs.
Can Exercise Help?
Physical activity can help your loved one keep some muscle strength and coordination. It might also boost his mood and help him feel less anxious. Check with his doctor to learn which types of exercise are appropriate. Repetitive activities, like walking, gardening, or even folding laundry may be the best at giving him a sense of calm.
How Is It Treated?
There’s no cure for Alzheimer’s and no way to slow the nerve damage it causes in the brain. But there are medications that appear to help maintain mental skills and slow the disease’s effects. If your loved one gets treatment early on, she may be able to stay independent and do her daily tasks for a longer period of time.
The Caregiver's Role
If you’re caring for someone with this disease, you’ll probably wear many hats -- cook, chauffeur, and accountant to name a few. While you may have to handle meal planning and finances, encourage your loved one to do some things for herself. It may help to label cabinets with their contents and put up sticky notes with reminders of daily tasks. Be sure to buy a weekly pill box for her medications.
Challenges in Caregiving
In the early stages, people with Alzheimer’s often understand what’s happening to them. They may be ashamed or get anxious. Watch for signs of depression, which the doctor can manage with medication. Later on, your loved one may become paranoid or aggressive and could even turn on you. Remember that the disease is responsible for this change. Tell the doctor about this kind of behavior promptly.
Sundown Syndrome
Experts don’t know why, but some people with Alzheimer’s get upset when the sun goes down. This tends to last through the evening and sometimes all night long. To ease tension, keep the house well lit and close the drapes before sunset. Try to distract your loved one with a favorite activity or TV show. Switch him to decaf after breakfast.
When Your Loved One Doesn't Know You
Many people with Alzheimer’s have trouble remembering names, even of people closest to them. A temporary fix is to put up pictures of people they’re likely to see often or know well with names printed underneath. Eventually, your loved one may no longer recognize faces and may react as if family members are strangers. This can be distressing, especially for the main caregiver.
Warning Signs of Caregiver Stress
Caring for someone with Alzheimer's can be physically and mentally draining. Signs of caregiver stress include:
Anger, sadness, and mood swings
Headaches or back pain
Trouble concentrating
Trouble sleeping
Take Care of Yourself
To avoid caregiver burnout, make sure you take at least a few minutes to do something you enjoy every day. Stay in touch with friends and keep up with hobbies when you can. Find a friend or relative to be your support person. You can also join an online or local caregiver support group through the Alzheimer’s Association.
Essential Documents
While your loved one is still able to make important decisions, talk to an attorney about drafting advance directives. These are legal documents that spell out what he wants in terms of medical treatments and end-of-life care. He should name someone to make health care decisions and manage finances on his behalf. This will help avoid confusion later on if he’s no longer able to state his wishes.
Home Health Care
Many people want to stay in their own homes as long as possible. That’s not easy if they have trouble getting dressed or using the bathroom on their own. A home health aide can help with personal hygiene and other daily tasks. You can also check with your local Area Agency on Aging for information on services that deliver meals or provide transportation to the elderly.
Assisted-Living Facilities
There may come a day when your loved one can no longer be cared for at home. If she doesn’t need 24-hour nursing care, an assisted-living facility may be good choice. They provide housing, meals, and activities, but are much less expensive than nursing homes. Look for one with an Alzheimer’s special care unit that can give 24-hour supervision and personal care to meet the needs of people with dementia.
The Later Stages
People with advanced Alzheimer’s may lose their ability to walk, talk, or respond to others. Eventually, the disease can hinder vital functions, like the ability to swallow. This may be the time to switch to hospice care, which provides pain relief and comfort for people with terminal illnesses.
How to Help Children Understand
Children may feel confused, afraid, or even resentful when a family member has Alzheimer’s. Let the child know these feelings are normal and answer her questions about the illness honestly. Help her celebrate happy memories of your loved one. You could create a scrapbook with pictures from happier times.
Can You Prevent It?
Is there anything you can do to lower your chances of getting this disease? Research in this area is ongoing, but diet and exercise appear to be important. Studies show people who eat a Mediterranean diet rich in vegetables, fish, and nuts and get plenty of physical activity are the least likely to get Alzheimer’s.