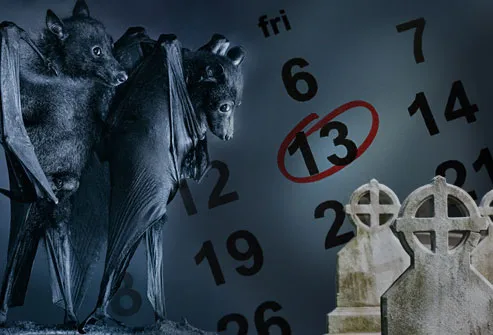How to Face Your Fears
Fear vs. Phobia
Fear protects you from danger. Phobias have little to do with danger. More than 19 million Americans have a phobia -- an intense, irrational fear when they face a certain situation, activity, or object. With a phobia, you may know your anxiety and fear are not warranted, but you can't help the feelings. And they can be so intense they virtually paralyze you. See what makes some people afraid in the slides ahead.
The Three Kinds of Phobia
Hundreds of different phobias have been identified, including phobophobia or fear of phobias. But when talking about phobias, which are a kind of anxiety disorder, experts divide them into three categories -- agoraphobia, an intense anxiety in public places where an escape might be difficult; social phobia, a fear and avoidance of social situations; and specific phobia, an irrational fear of specific objects or situations.
Agoraphobia: Fear of Public Places
The agora was a market and meeting place in ancient Greece. Someone with agoraphobia is afraid of being trapped in a public place or a place like a bridge or a line at the bank. The actual fear is of not being able to escape if anxiety gets too high. Agoraphobia affects twice as many women as men. If left untreated in extreme cases, it can lead to someone becoming housebound.
Social Phobia: Beyond Being Shy
Someone with a social phobia is not just shy. That person feels extreme anxiety and fear about how he or she will perform in a social situation. Will her actions seem appropriate to others? Will others be able to tell he's anxious? Will the words be there when it's time to talk? Because untreated social phobia often leads to avoiding social contact, it can have a major negative impact on a person's relationships and professional life.
Claustrophobia: Needing a Way Out
Claustrophobia, an abnormal fear of being in enclosed spaces, is a common specific phobia. A person with claustrophobia can't ride in elevators or go through tunnels without extreme anxiety. Afraid of suffocating or being trapped, the person will avoid tight spaces and often engage in "safety seeking behavior," such as opening windows or sitting near an exit. That may make the situation tolerable, but it doesn't relieve the fear.
Zoophobia: A Menagerie of Fears
The most common type of specific phobia is zoophobia or fear of animals. Zoophobia is actually a generic term that encompasses a group of phobias involving specific animals. Examples include arachnophobia -- fear of spiders; ophidiophobia -- fear of snakes; ornithophobia -- fear of birds, and apiphobia -- fear of bees. Such phobias often develop in childhood and sometimes go away as the child ages. But they can persist into adulthood.
Brontophobia: Fear of Thunder
The Greek word bronte means thunder and brontophobia means fear of thunder. Even though people with brontophobia may realize thunder won't hurt them, they may refuse to go outside during a thunderstorm. They may even hide indoors by crouching behind a couch or waiting out the storm in a closet. An abnormal fear of both thunder and lightning is called astraphobia, a phobia shared by people and animals.
Acrophobia: Fear of Heights
Acrophobia is an excessive fear of heights and manifests as severe anxiety. A person could have an attack just walking up stairs or climbing a ladder. Sometimes the fear is so great a person can't move. Acrophobia can create a dangerous situation for someone who has it. An anxiety attack can make it extremely difficult to safely get down from whatever high place triggered the attack.
Aerophobia: Afraid to Fly
Someone who has aerophobia is afraid of flying. The phobia generally develops after a person has a traumatic experience involving an airplane, such as going through extreme turbulence or witnessing another passenger have a panic attack. Even after the incident is forgotten, the fear stays and can even be triggered by watching film of a plane crash on TV. Hypnotherapy is commonly used to identify the initial trauma and to treat this phobia.
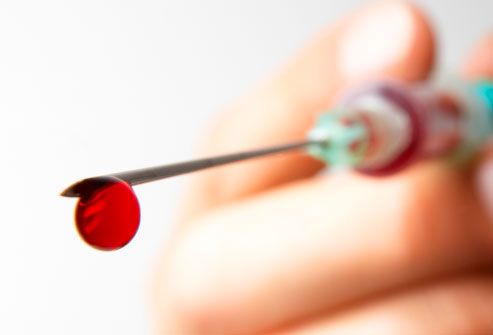
Blood-Injection-Injury Phobias
There is a spectrum of blood, injection, and injury phobias including hemophobia (fear of blood) and trypanophobia (fear of receiving an injection). Some people have an injury phobia, and others have a phobia about invasive medical procedures. These phobias are associated with fainting.
Paranormal Fears
Some phobias sound like they belong on the chiller channel on cable TV. Triskaidekaphobia is an abnormal fear of anything related to the number 13. If the thought of ghosts makes you overly anxious, you may have phasmophobia. And despite the fact that vampires aren't real, some people are terrified of bats. Their phobia is called chiroptophobia.
Emetophobia: A Gut Feeling
Emetophobia is an unnatural fear of vomiting that typically starts early in life from some traumatic episode. For instance, someone may have witnessed a schoolmate vomiting in public or done so himself. The anxiety can be triggered by thoughts of vomiting or thinking of somewhere such as a hospital, where vomiting is common. As with aerophobia, hypnotherapy is commonly used in part of the treatment.
Carcinophobia: Fear of Cancer
People with carcinophobia or cancerophobia live with an irrational dread of developing cancer. Every bodily discomfort becomes a sign for them that they have a malignant growth somewhere inside. A headache, for instance, is a sign for them that they have a brain tumor. Cognitive therapy can help someone with carcinophobia regain control of their life.
Phobias From New to Old
Someone who fears anything new has a neophobia. And someone who is afraid of growing old or afraid of old people has a gerontophobia. Somewhere in between, you might find someone with phartophobia, which is an unreasonable fear of passing gas in a public place. Someone with odontiatophobia will go out of his way to avoid going to a dentist. And a spargarophobic individual will panic over a plate of asparagus.
Life-Altering Effects of Phobias
Phobias cause people to change how they live in order to avoid the object of their fear. But their life is also affected by their attempts to conceal the phobia from others. Some people with phobias have problems with friends and family, fail in school, or lose jobs while struggling to cope.
Phobias and Alcohol
Alcoholics can be up to 10 times more likely to suffer from a phobia than those who are not alcoholics. And phobic individuals can be twice as likely to be addicted to alcohol as those who have never been phobic.
A Family Connection
Although phobias can be influenced by culture and triggered by life events, they tend to run in families. Immediate family members of people with phobias are about three times more likely to have a phobia than those without a family history.
Treating Phobias
Desensitization is a process of gradually exposing someone with a phobia to circumstances that resemble what he fears. Over time, the fear lessens as the person builds confidence. This is often accompanied by talk therapy to help the person change how he or she thinks and develop new patterns of response to situations that might trigger the emotions associated with a phobia. The good news is treatment helps 90% of people who follow through.
Learn More About Phobias
These associations can provide you more information about phobias:
American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, www.aacap.org
American Counseling Association, www.counseling.org
Fear protects you from danger. Phobias have little to do with danger. More than 19 million Americans have a phobia -- an intense, irrational fear when they face a certain situation, activity, or object. With a phobia, you may know your anxiety and fear are not warranted, but you can't help the feelings. And they can be so intense they virtually paralyze you. See what makes some people afraid in the slides ahead.
The Three Kinds of Phobia
Hundreds of different phobias have been identified, including phobophobia or fear of phobias. But when talking about phobias, which are a kind of anxiety disorder, experts divide them into three categories -- agoraphobia, an intense anxiety in public places where an escape might be difficult; social phobia, a fear and avoidance of social situations; and specific phobia, an irrational fear of specific objects or situations.
Agoraphobia: Fear of Public Places
The agora was a market and meeting place in ancient Greece. Someone with agoraphobia is afraid of being trapped in a public place or a place like a bridge or a line at the bank. The actual fear is of not being able to escape if anxiety gets too high. Agoraphobia affects twice as many women as men. If left untreated in extreme cases, it can lead to someone becoming housebound.
Social Phobia: Beyond Being Shy
Someone with a social phobia is not just shy. That person feels extreme anxiety and fear about how he or she will perform in a social situation. Will her actions seem appropriate to others? Will others be able to tell he's anxious? Will the words be there when it's time to talk? Because untreated social phobia often leads to avoiding social contact, it can have a major negative impact on a person's relationships and professional life.
Claustrophobia: Needing a Way Out
Claustrophobia, an abnormal fear of being in enclosed spaces, is a common specific phobia. A person with claustrophobia can't ride in elevators or go through tunnels without extreme anxiety. Afraid of suffocating or being trapped, the person will avoid tight spaces and often engage in "safety seeking behavior," such as opening windows or sitting near an exit. That may make the situation tolerable, but it doesn't relieve the fear.
Zoophobia: A Menagerie of Fears
The most common type of specific phobia is zoophobia or fear of animals. Zoophobia is actually a generic term that encompasses a group of phobias involving specific animals. Examples include arachnophobia -- fear of spiders; ophidiophobia -- fear of snakes; ornithophobia -- fear of birds, and apiphobia -- fear of bees. Such phobias often develop in childhood and sometimes go away as the child ages. But they can persist into adulthood.
Brontophobia: Fear of Thunder
The Greek word bronte means thunder and brontophobia means fear of thunder. Even though people with brontophobia may realize thunder won't hurt them, they may refuse to go outside during a thunderstorm. They may even hide indoors by crouching behind a couch or waiting out the storm in a closet. An abnormal fear of both thunder and lightning is called astraphobia, a phobia shared by people and animals.
Acrophobia: Fear of Heights
Acrophobia is an excessive fear of heights and manifests as severe anxiety. A person could have an attack just walking up stairs or climbing a ladder. Sometimes the fear is so great a person can't move. Acrophobia can create a dangerous situation for someone who has it. An anxiety attack can make it extremely difficult to safely get down from whatever high place triggered the attack.
Aerophobia: Afraid to Fly
Someone who has aerophobia is afraid of flying. The phobia generally develops after a person has a traumatic experience involving an airplane, such as going through extreme turbulence or witnessing another passenger have a panic attack. Even after the incident is forgotten, the fear stays and can even be triggered by watching film of a plane crash on TV. Hypnotherapy is commonly used to identify the initial trauma and to treat this phobia.
Blood-Injection-Injury Phobias
There is a spectrum of blood, injection, and injury phobias including hemophobia (fear of blood) and trypanophobia (fear of receiving an injection). Some people have an injury phobia, and others have a phobia about invasive medical procedures. These phobias are associated with fainting.
Paranormal Fears
Some phobias sound like they belong on the chiller channel on cable TV. Triskaidekaphobia is an abnormal fear of anything related to the number 13. If the thought of ghosts makes you overly anxious, you may have phasmophobia. And despite the fact that vampires aren't real, some people are terrified of bats. Their phobia is called chiroptophobia.
Emetophobia: A Gut Feeling
Emetophobia is an unnatural fear of vomiting that typically starts early in life from some traumatic episode. For instance, someone may have witnessed a schoolmate vomiting in public or done so himself. The anxiety can be triggered by thoughts of vomiting or thinking of somewhere such as a hospital, where vomiting is common. As with aerophobia, hypnotherapy is commonly used in part of the treatment.
Carcinophobia: Fear of Cancer
People with carcinophobia or cancerophobia live with an irrational dread of developing cancer. Every bodily discomfort becomes a sign for them that they have a malignant growth somewhere inside. A headache, for instance, is a sign for them that they have a brain tumor. Cognitive therapy can help someone with carcinophobia regain control of their life.
Phobias From New to Old
Someone who fears anything new has a neophobia. And someone who is afraid of growing old or afraid of old people has a gerontophobia. Somewhere in between, you might find someone with phartophobia, which is an unreasonable fear of passing gas in a public place. Someone with odontiatophobia will go out of his way to avoid going to a dentist. And a spargarophobic individual will panic over a plate of asparagus.
Life-Altering Effects of Phobias
Phobias cause people to change how they live in order to avoid the object of their fear. But their life is also affected by their attempts to conceal the phobia from others. Some people with phobias have problems with friends and family, fail in school, or lose jobs while struggling to cope.
Phobias and Alcohol
Alcoholics can be up to 10 times more likely to suffer from a phobia than those who are not alcoholics. And phobic individuals can be twice as likely to be addicted to alcohol as those who have never been phobic.
A Family Connection
Although phobias can be influenced by culture and triggered by life events, they tend to run in families. Immediate family members of people with phobias are about three times more likely to have a phobia than those without a family history.
Treating Phobias
Desensitization is a process of gradually exposing someone with a phobia to circumstances that resemble what he fears. Over time, the fear lessens as the person builds confidence. This is often accompanied by talk therapy to help the person change how he or she thinks and develop new patterns of response to situations that might trigger the emotions associated with a phobia. The good news is treatment helps 90% of people who follow through.
Learn More About Phobias
These associations can provide you more information about phobias:
American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, www.aacap.org
American Counseling Association, www.counseling.org